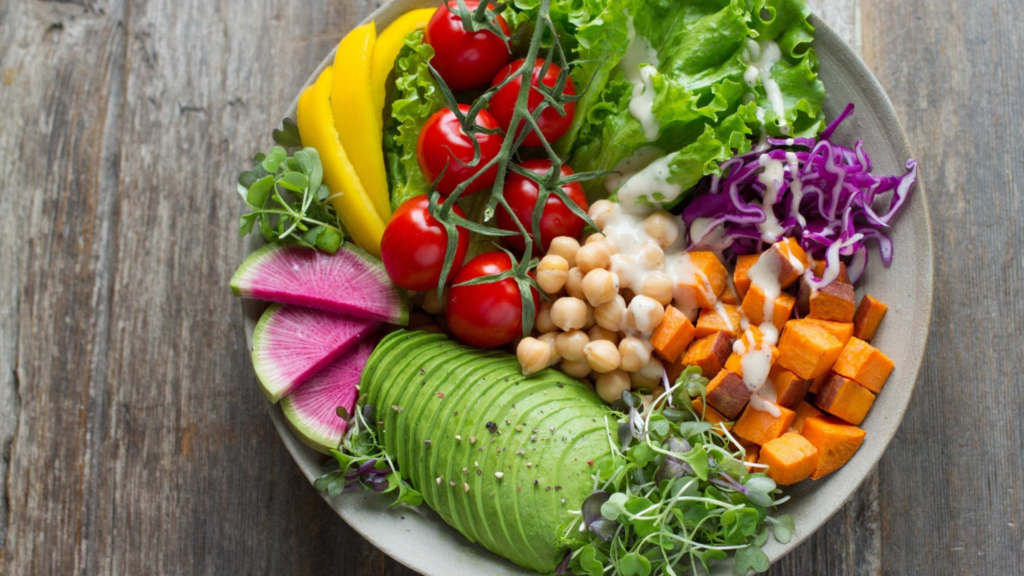
Gut health plays a vital role in digestion, immunity, and overall well-being. While eating the right foods is crucial, how you prepare them is just as important. The way you cook can either preserve or destroy essential nutrients, prebiotics, and probiotics that support a healthy gut microbiome.
This blog explores the science behind gut-friendly cooking and highlights key techniques that optimize digestion. Methods such as steaming, slow cooking, fermenting, and sprouting help retain nutrients, enhance absorption, and promote beneficial gut bacteria. Additionally, selecting the right kitchen tools—such as fermentation jars, slow cookers, sprouting trays, and non-toxic cookware—ensures that your meals support gut health without introducing harmful chemicals.
By making simple changes in your cooking habits, you can improve digestion, boost metabolism, and strengthen your immune system. Incorporating gut-friendly techniques into your daily routine will help you maintain a balanced and thriving microbiome for long-term health and well-being. Start cooking for a healthier gut today!
1. Understanding Gut Health and the Role of Cooking
1. What Is Gut Health?
The gut microbiome is a complex ecosystem of trillions of bacteria that play a vital role in digestion, nutrient absorption, immune function, and even mental health. A well-balanced microbiome supports overall well-being, helping to break down food, synthesize essential vitamins, and protect against harmful pathogens. While diet is one of the primary factors that shape gut flora, cooking techniques can significantly influence the nutritional quality of food and its effects on gut bacteria. Choosing the right cooking methods can help preserve gut-friendly nutrients, prebiotics, and probiotics, ensuring that your meals actively support digestive health.
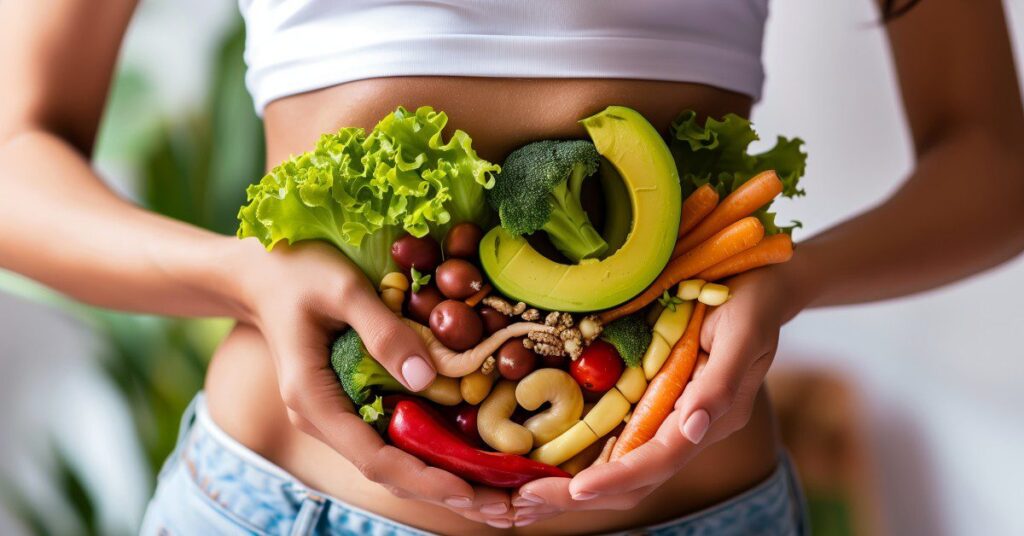

2. How Cooking Affects Gut Health
Cooking methods impact the availability of essential nutrients, fiber, and live beneficial bacteria in food. Certain techniques help retain prebiotics and probiotics—key components that nourish gut flora and promote a balanced microbiome.
Steaming vs. Boiling: Steaming vegetables preserves more fiber, vitamins, and prebiotic compounds compared to boiling, which can leach nutrients into the water. Steamed vegetables provide better support for gut bacteria, aiding digestion and nutrient absorption.
Fermentation: Foods like kimchi, yogurt, and sauerkraut contain live probiotics that replenish beneficial gut bacteria. However, proper fermentation and storage methods are necessary to maintain their probiotic benefits. Pasteurization or excessive heat can destroy these good bacteria, making homemade or traditionally fermented options a superior choice.
Slow Cooking & Bone Broth: Cooking at lower temperatures for longer periods helps preserve collagen and amino acids, which aid in gut lining repair. Bone broth, rich in gelatin and glutamine, supports gut integrity and digestive function.
By making small adjustments in how you prepare food, you can optimize gut health, improve digestion, and enhance nutrient absorption, ultimately promoting long-term wellness.
2. Gut-Friendly Cooking Techniques
The way you cook your food significantly impacts its nutritional quality and effects on gut health. By using gentle cooking techniques, you can preserve fiber, prebiotics, and probiotics that support digestion and a thriving microbiome. Here are some of the best cooking methods for gut health:
1. Steaming & Sautéing
These techniques help retain essential nutrients and fiber, making food easier to digest.
- Steaming: Using a steamer basket prevents the loss of water-soluble vitamins and prebiotics, ensuring vegetables maintain their gut-friendly benefits.
- Sautéing: Light sautéing in healthy oils like olive or avocado oil allows for gentle cooking without excessive heat damage, helping to preserve gut-friendly compounds while enhancing flavor.
2. Slow Cooking & Bone Broth
Slow cooking at low temperatures helps preserve collagen, amino acids, and essential nutrients that support gut health.
- Bone Broth: Rich in gelatin and glutamine, bone broth aids in repairing the gut lining, reducing inflammation, and improving digestion.
- Gut-Healing Stews: Cooking meats and vegetables slowly in broth allows for better nutrient absorption while making food easier to digest.
- Best Tools: A slow cooker or Instant Pot simplifies the process of preparing nourishing broths and stews.
3. Fermentation
Fermented foods are packed with probiotics that replenish beneficial gut bacteria and support digestion.
- Kimchi, Sauerkraut, & Kombucha: These probiotic-rich foods require careful fermentation and storage to maintain their live cultures.
- Controlled Fermentation: Using fermentation jars ensures the right environment for cultivating healthy bacteria.
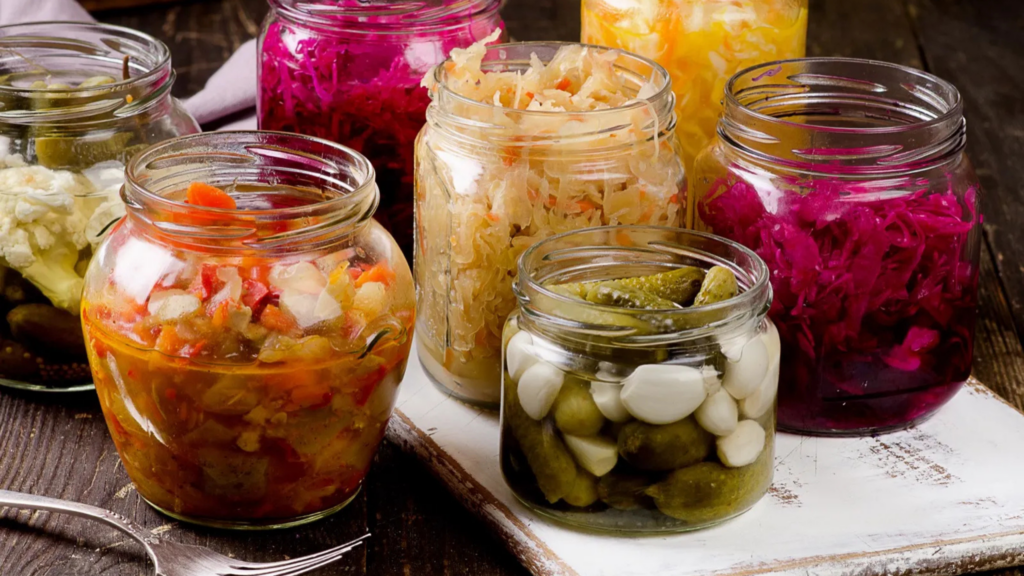

4. Sprouting
Sprouting grains, seeds, and legumes enhances nutrient absorption and improves digestibility.
- Nutrient Boost: Sprouting breaks down phytic acid, which can inhibit mineral absorption.
- Simple Process: A sprouting jar or tray makes it easy to grow gut-friendly sprouts like alfalfa, broccoli, and lentils at home.
5. Blending
Blending helps create nutrient-dense, fiber-rich, and easy-to-digest meals.
- Smoothies & Soups: A high-powered blender or food processor can make gut-friendly smoothies, pureed soups, and probiotic dips that support digestion and gut health.
By incorporating these techniques into your cooking routine, you can enhance nutrient absorption, protect your gut microbiome, and promote overall digestive well-being.
3. Best Foods for Gut Health & How to Prepare Them
Incorporating gut-friendly foods into your diet can significantly improve digestion, support beneficial gut bacteria, and enhance overall health. Here are some of the best foods for gut health and how to prepare them for maximum benefits.
1. Fiber-Rich Vegetables
- Examples: Carrots, spinach, onions
- Benefits: High in prebiotic fiber, which nourishes good bacteria and supports digestion.
- Preparation: Steam vegetables using a steamer basket to preserve fiber, vitamins, and antioxidants while making them easier to digest.

2. Fermented Foods
- Examples: Yogurt, kimchi, sauerkraut
- Benefits: Rich in probiotics that help restore and maintain a balanced gut microbiome.
- Preparation: Store fermented foods in mason jars to keep them fresh and prevent exposure to harmful bacteria.
3. Bone Broth
- Benefits: Contains collagen, gelatin, and amino acids that help repair the gut lining, reduce inflammation, and support digestion.
- Preparation: Simmer bones in a slow cooker or Instant Pot for 12-24 hours with apple cider vinegar to extract maximum nutrients.
4. Legumes & Whole Grains
- Examples: Lentils, chickpeas, quinoa, oats
- Benefits: High in fiber and resistant starch, which act as prebiotics to feed beneficial gut bacteria.
- Preparation: Cook legumes and grains in a non-toxic ceramic, cast iron, or stainless steel pot to avoid unwanted chemicals from non-stick coatings.
5. Homemade Dairy-Free Milk
- Examples: Almond milk, oat milk
- Benefits: Easier to digest for those with lactose intolerance while still providing essential nutrients.
- Preparation: Use a nut milk bag to strain homemade almond or oat milk, ensuring a smooth and natural alternative to store-bought versions.
By preparing these gut-friendly foods with the right methods, you can optimize nutrient absorption, promote a thriving gut microbiome, and support overall well-being.
4. Essential Kitchen Tools for Gut-Healthy Cooking
Using the right kitchen tools can enhance your cooking methods, helping to preserve nutrients, prebiotics, and probiotics that support gut health. Here are some must-have kitchen essentials for optimizing digestion and promoting a healthy microbiome:
- Fermentation Jars – Essential for making homemade kimchi, sauerkraut, and kombucha, ensuring a controlled environment for beneficial bacteria to thrive.
- Blender or Food Processor – Ideal for creating fiber-rich smoothies, probiotic dips, and gut-friendly soups while breaking down fiber for easier digestion.
- Steamer Basket – Helps preserve nutrients in vegetables by preventing excessive nutrient loss from boiling.
- Titanium Cutting Board – A hygienic, non-porous surface that prevents bacterial contamination and is easy to clean.

- Slow Cooker or Instant Pot – Perfect for making bone broth and gut-friendly stews, allowing collagen and amino acids to develop slowly for maximum gut-healing benefits.
- Sprouting Jar or Tray – Helps grow nutrient-dense sprouts like alfalfa and broccoli, which support gut health.
- Non-Toxic Cookware – Prevents chemical exposure from non-stick coatings, ensuring a cleaner, healthier cooking process.
- Nut Milk Bag – Useful for making homemade almond or oat milk, which is easier to digest than conventional dairy.
- Silicone Spatulas – Prevents damage to cookware and is easy to clean, reducing the risk of bacteria buildup.
- Mason Jars – Great for storing overnight oats, fermented foods, and probiotic-rich recipes in a convenient and airtight way.
5. Easy Gut-Healthy Recipes to Try
1. Homemade Bone Broth
Ingredients: Bones, water, apple cider vinegar, garlic.
Method: Simmer in a slow cooker for 12-24 hours.
Benefits: Supports gut lining with collagen and amino acids.
2. Probiotic-Rich Yogurt Bowl
Ingredients: Greek yogurt, chia seeds, berries, and honey.
Method: Mix in a mason jar and refrigerate overnight.
Benefits: Provides probiotics and fiber.
3. Fermented Cabbage (Easy Sauerkraut)
Ingredients: Cabbage, salt, filtered water.
Method: Store in a fermentation jar for 7-14 days.
Benefits: Supplies live probiotics to aid digestion.
4. Green Gut Smoothie
Ingredients: Spinach, banana, almond milk, kefir, flaxseeds.
Method: Blend everything using a high-speed blender.
Benefits: Rich in fiber and probiotics.

6. Final Thoughts: Cooking for a Healthier Gut
Cooking for gut health goes beyond choosing the right foods—it’s also about using the best preparation methods to preserve essential nutrients, fiber, and beneficial bacteria. The way you cook can impact your gut microbiome, influencing digestion, immunity, and overall well-being.
Incorporating gut-friendly kitchen tools, such as fermentation jars, slow cookers, sprouting trays, and non-toxic cookware, helps you create meals that nourish your digestive system. Techniques like steaming, fermenting, slow cooking, and sprouting maximize nutrient retention and support good gut bacteria, promoting a balanced and thriving microbiome.
Ready to upgrade your gut health? Start by integrating these tools and techniques into your daily routine. Prioritizing gut-friendly cooking can optimize digestion, reduce inflammation, and enhance overall wellness, leading to a healthier future. Small changes in your cooking habits can make a significant impact—so take the first step today toward better gut health and long-term well-being!